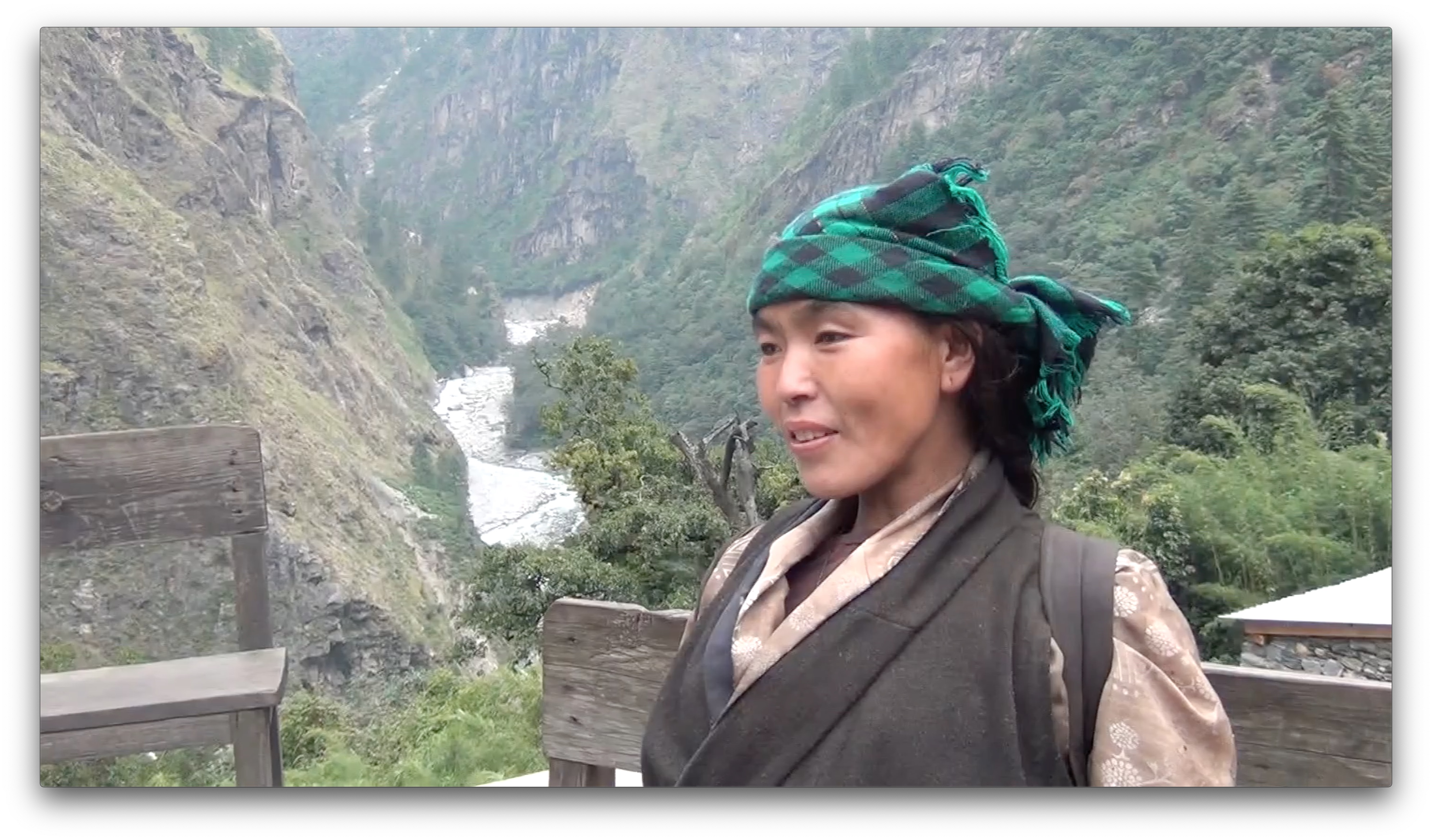
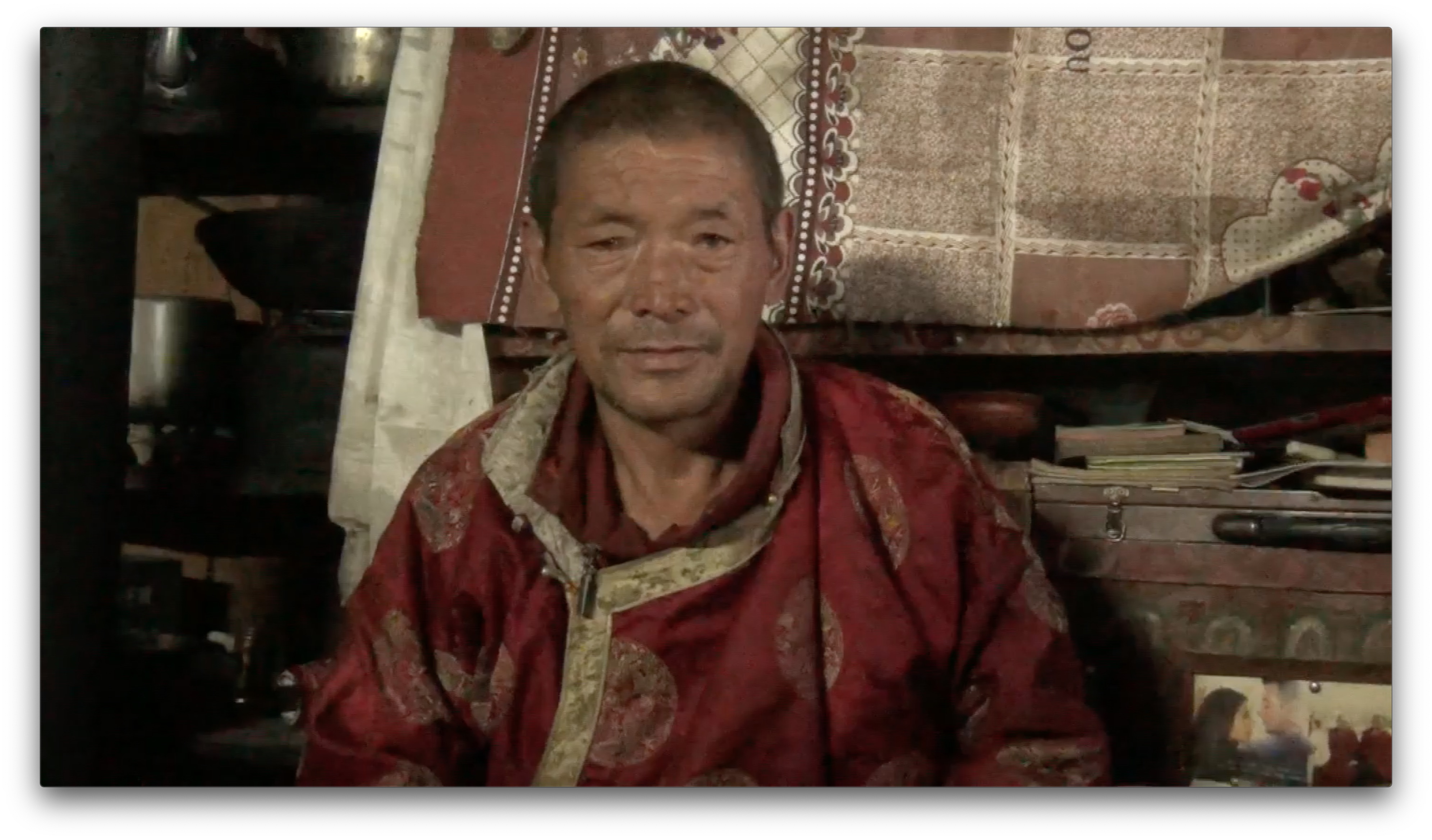
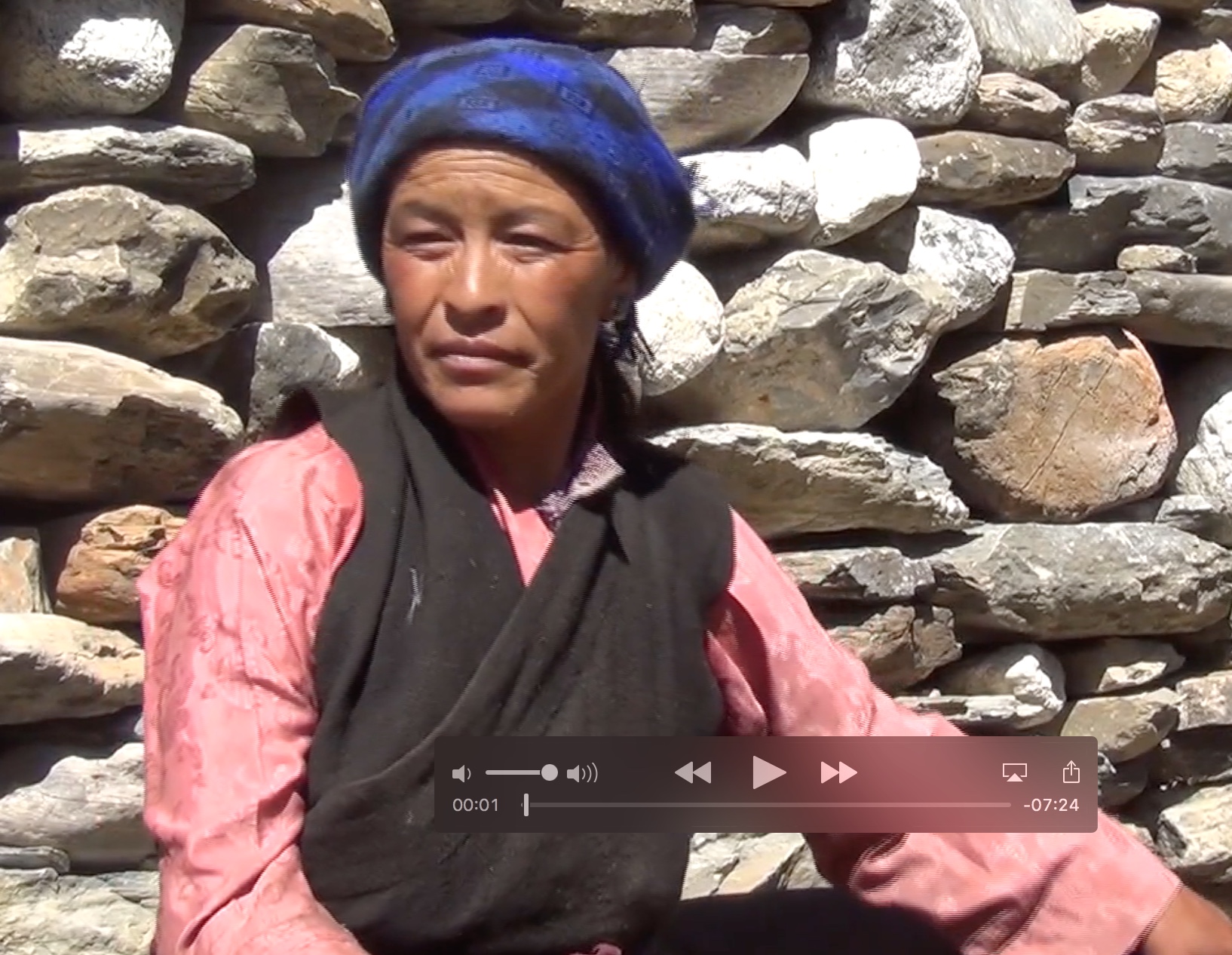
Explore Tsum: Reflections on the 2015 Nepal Earthquakes
The purpose of this collection is to feature selected discourses and interviews as provided by members of the Tsum community of the Southwestern District, Nepal.
About This Collection
This collection is the result of a National Science Foundation RAPID project (BCS 1547377) to collect, annotate, and make publicly available multi-participant interviews and narratives conducted with survivors of Nepal’s major earthquakes that occurred in April and May 2015. The geo-linguistic focus is communities of Tibeto-Burman language-speaking peoples from three contiguous districts of Nepal’s Western Zone: Mustang, Manang and Gorkha, including local residents and also migrants who are now involved in relief and rebuilding efforts. The research questions are: 1) What do survivors and responders know about, and how can they explain the earthquakes based on their lifelong linguistic, cultural and environmental experiences? 2) How do survivors and responders view their world through these earthquakes and their aftermath, particularly in terms of causality and consequence? This research is important because there is precious little information about the impacts on language demographics and practices in sudden catastrophic events that coincide with great migration movements. Additionally, without an immediate effort to capture and document variation and nuances, the experiences that different people underwent will be influenced and re-shaped by reports gathered from the media and other relief agencies working in Nepal. This study focuses on the relationship between humans and their social and physical environment, providing valuable insider perspectives on why and how they create and maintain their livelihoods in places where extreme environmental conditions are a constant and powerful presence. The interviews and narratives will enable disaster planners and responders to establish best-practice advice, based on local and culturally appropriate ethnographic practice, one that is tailored to the demographic, spatial, medical and cultural needs of different communities. This study will provide ideas, originating from local participants, about how local healers and responders can provide ritual and medical services that will be beneficial to the highland communities, which are an important part of the overall Nepal demography.
The variables integrated into the interviews include: location and origin of the survivor or responder, and distance from the quake epicenter; kind of terrain of the village (mountain valley, hills, flat; ridge top, valley floor, slope); social environment (city; town; village; field outpost); structures in place or damaged (traditional, modern), and building materials (wood or stone, on walls or as roofs); responses already in action and kinds of planned responses; local religion(s); local labor force; medical facilities in place; local language practices; feelings about post-quake response by local and non-local agencies and individuals, assessment of future community vitality. The research toolsh have been approved for human subjects and informed consent review at all institutions for which the project members are affiliated.
The narrative process asks individuals to share, in monologue or dialogue form, their experiences, descriptions of their actions and responses, their self-evaluation of the usefulness of their actions, their understanding/perception of why these events took place, their perception of why their local area was impacted in the way that it was, and how they would like to see repair/reconstruction occur, with what agency, and with what stated goals. As with the interviews, topic choices and degree of detail will be controlled by the participants, based on their ability and willingness to share vivid memories and sometimes-controversial opinions.
Background Information on Tsum
Tsum is a variety of the Sino-Tibetan language. This language is primarily spoken in the South Western location of Nepal (28.47, 185.08). The ISO-639 code assigned to the Tsum language is (ttz) and the glottocode is (Tsum 1240). The Tsum language is originally derived from the Gyalsumdo-Nubri-Kyirong language, and the Gyalsumdo-Nubri-Kyirong language is originally derived from the Kyirong-Kagate language. The derivation of each language is altogether a separate language. Kyirong-Kagate is primarily spoken in Nepal with approximately 15000 native speakers, and Tsum is one of the multiple dialects in the Kyirong-Kagate language.
Selected References
Driem, George Van. 2001. Languages of the Himalayas. (Handbuch der Orientalistik: Section Two: India, 10.) E. J. Brill. 1350pp. (2 Vols.)
Dhakal, Dubi Nanda. & Donohue Mark. 2015. Nepalese Linguistics. Volume 30. Inchoative/causative verb pairs in Tsum, 45-49 http://lsn.org.np/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/NepLing30.pdf (2016, May)
Gawne, Lauren. 2010. Nepalese Linguistics. Volume 25. Lamjung Yolmo: a dialect of Yolmo, also known as Helambu Sherpa, 34-41 http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/nepling/pdf/Nep_Ling_25.pdf
Hill, Nathan & Owen-Smith, Thomas. 2014. Trans-Himalayan linguistics: historical and descriptive linguistics of the Himalayan area. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton
Lapolla, Randy J. & Thurgood, Graham. 2007. The Sino-Tibetan languages.Oxford, UK: Routledge
Tsum. 2016. Glottolog
Webster, Jeff. 1992. A socio-linguistic survey of the Tibeto-Burman dialects of North Gorkha District, Nepal. Unpublished manuscript.
World Heritage Encyclopedia. 2016. Kyirong-Kagate Language
Audio-Video Items in this collection
The list below includes items from this Collection’s Subcollections.